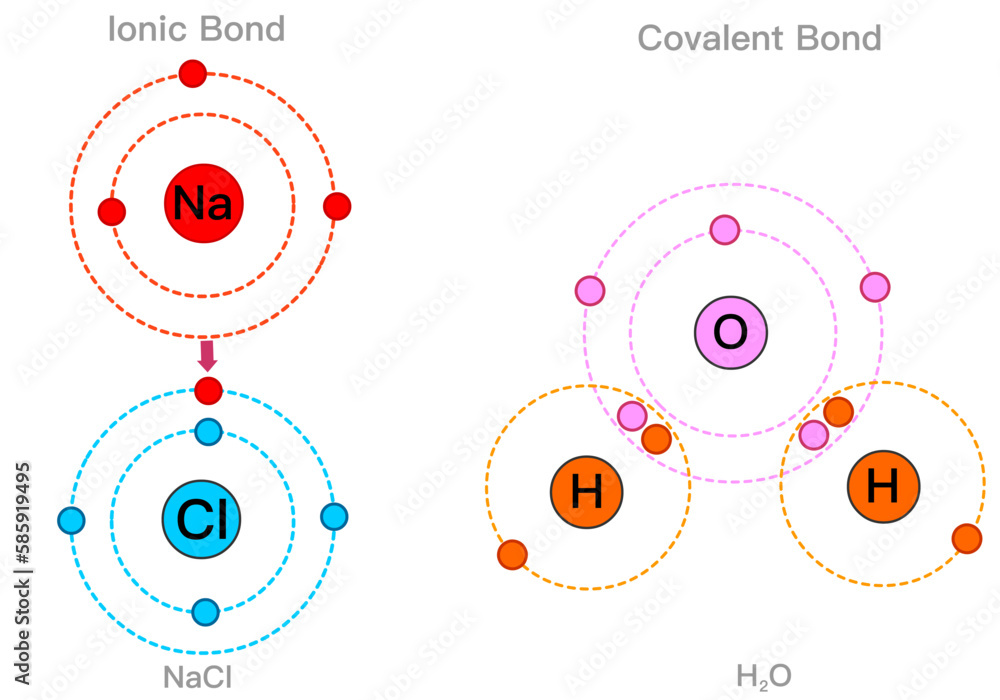
Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds . Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Bonding between metals and nonmetals is usually ionic, while bonding among nonmetals is usually covalent. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure.
from stock.adobe.com
Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Bonding between metals and nonmetals is usually ionic, while bonding among nonmetals is usually covalent. Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table.
Vecteur Stock Ionic covalent bonds examples. Chemical structural models
Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Bonding between metals and nonmetals is usually ionic, while bonding among nonmetals is usually covalent. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the.
From slideplayer.com
Properties of Metalloids ppt download Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Each atom within the crystal has. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From www.youtube.com
More Naming Ionic Bonds (With Transition Metals) YouTube Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Each atom. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From viziscience.com
Naming compounds High School/Honors/AP® Chemistry Resources Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Bonding between metals and nonmetals is usually ionic, while bonding among nonmetals is usually covalent. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From slideplayer.com
1) B Quartz is the only covalent network solid present ppt download Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From slideplayer.com
Please take out your study guide. ppt download Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT The Periodic Table and Ionic Bonding Part 1Periodic Table Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Bonding between metals and nonmetals is usually ionic, while bonding among nonmetals is usually covalent. A series of six elements called. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From stock.adobe.com
Ionic bond and electrostatic attraction from chemical bonding outline Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Metalloids can. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From mmerevise.co.uk
Ionic Bonding Questions and Revision MME Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Metallic Bonds Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the. Bonding between metals and nonmetals is usually ionic, while bonding among nonmetals is usually covalent. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. In. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From scientifictutor.org
Chem Covalent, Ionic, and Metallic Bonds (Intramolecular Forces Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the.. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From fdocuments.in
Metals NonMetals and Metalloids. Metals Lose electrons during Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From stock.adobe.com
Vecteur Stock Ionic covalent bonds examples. Chemical structural models Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From www.chemistrylearner.com
Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonds Differences and Similarities Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). Each atom within the crystal has covalent. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Periodicity Chemistry Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From slideplayer.com
Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding ppt download Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Generally, the band gap increases as. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From slideplayer.com
Chemical Bonds Notes 10/16/ ppt download Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the. The metalloids are boron, silicon,. Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Bonding between. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From www.pinterest.de
Metallic Hydrogen, Metallic Bonding, Ionic Compound, Ionic Bonding Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an ionic. A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. Each atom within. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.
From www.periodictableprintable.com
Periodic Table Identify Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Periodic Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds Generally, the band gap increases as the 2 elements are farther apart (the bonding becomes more ionic, and ionic solids aren't conductive). Metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds. In substances containing only metal atoms, however, the interaction. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. For example, silicon dioxide is a covalent compound, while arsenic oxide is an. Are Metalloids In Ionic Bonds.